Evolutionary Computations

Evolutionary Computation (EC) refers to computer-based problem solving systems that use computational models of evolutionary processes, such as
- natural selection.
- survival of the fittest.
- reproduction.
Read more | August 3, 2014
Artificial Neural Networks
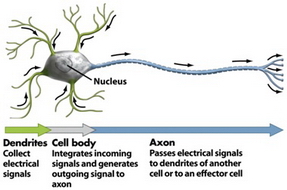
The brain is a complex, nonlinear and parallel computer. It has the ability to perform tasks such as pattern recognition, perception and motor control much faster than any computer.
Artificial neural networks (ANN) are computational models that attempt to capture the behavioral and adaptive features of biological nervous systems.
Read more | August 3, 2014
Fuzzy Systems
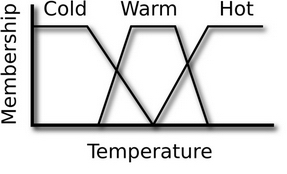
Fuzzy Sytem (FS) deals mainly with uncertainty and vagueness. We do not live in a world of ones and zeros, black and white, true and false, or other absolutes.
Read more | August 3, 2014
Artificial Immune Systems
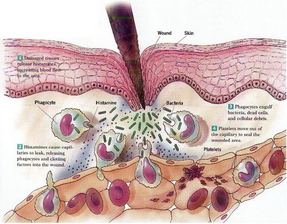
An Artificial Immune System (AIS) models the natural immune system’s ability to detect cells foreign to the body. The result is a new computational paradigm with powerful pattern recognition abilities, mainly applied to anomaly detection.
Read more | August 3, 2014
Swarm Intelligence
Swarm intelligence (SI) refers to the problem-solving behavior that emerges from the interaction of such agents.
More formally, swarm intelligence is the property of a system whereby the collective behaviors of unsophisticated agents interacting locally with their environment cause coherent functional global patterns to emerge.
Swarm intelligence has also been referred to as collective intelligence.
Read more | August 3, 2014


